Be yourself; Everyone else is already taken.
— Oscar Wilde.
This is the first post on my new blog. I’m just getting this new blog going, so stay tuned for more. Subscribe below to get notified when I post new updates.
Be yourself; Everyone else is already taken.
— Oscar Wilde.
This is the first post on my new blog. I’m just getting this new blog going, so stay tuned for more. Subscribe below to get notified when I post new updates.
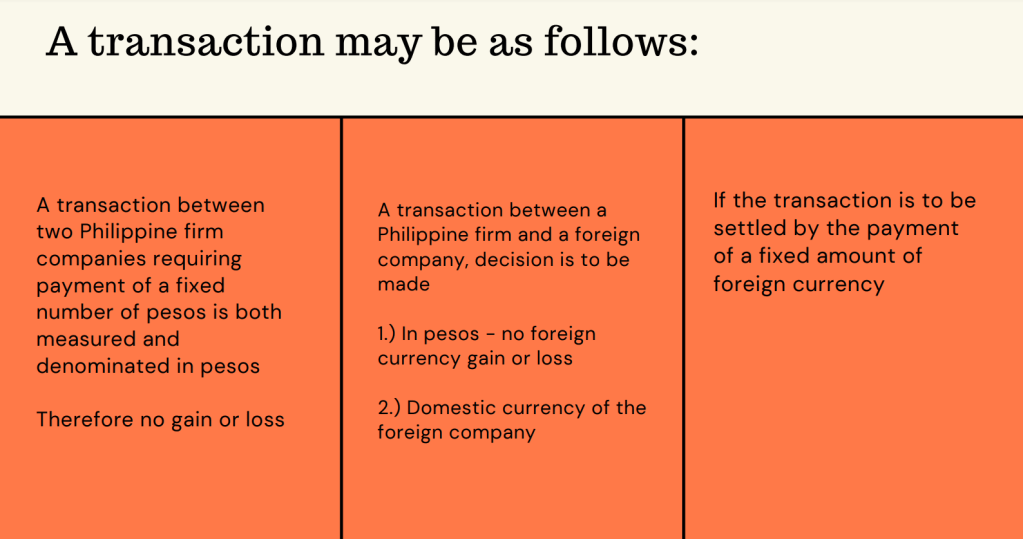
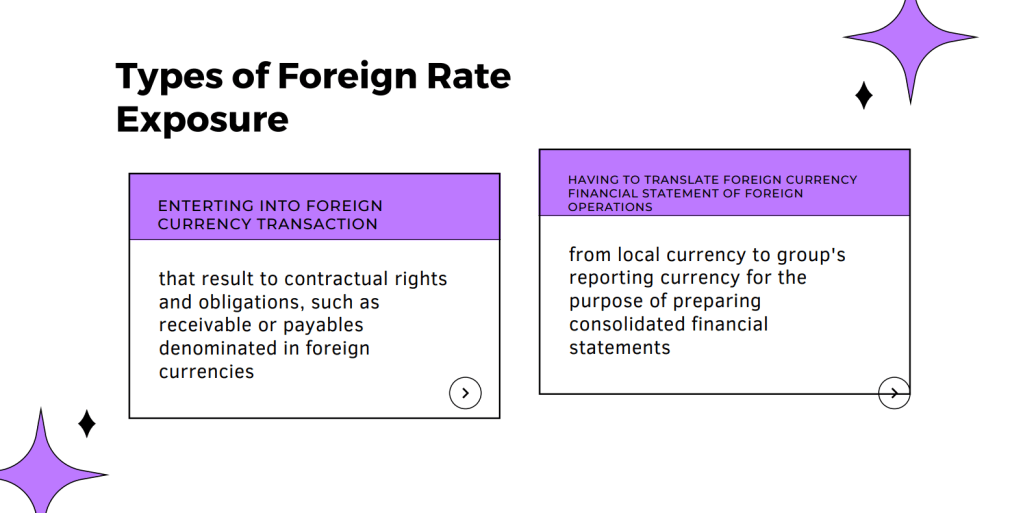
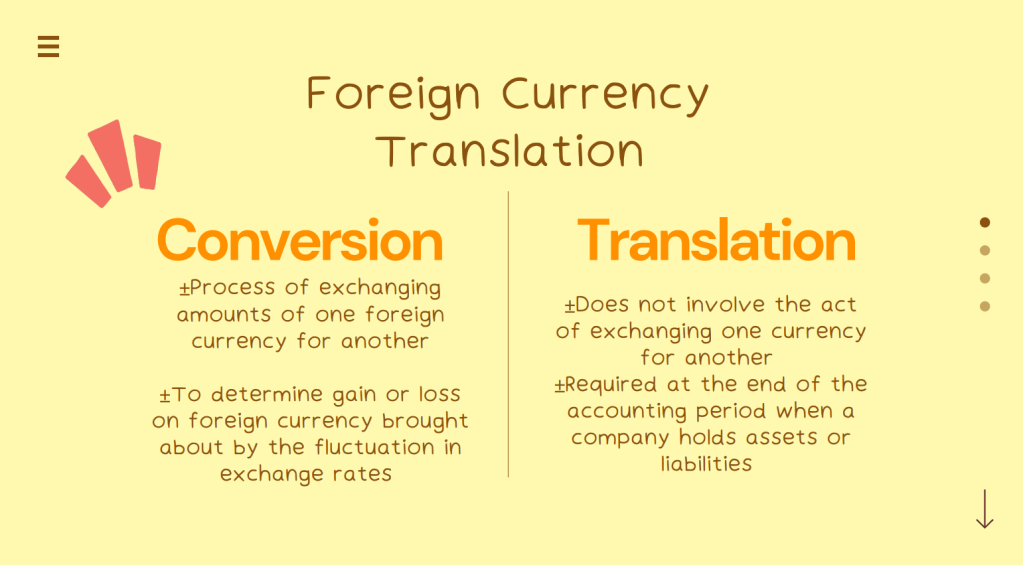




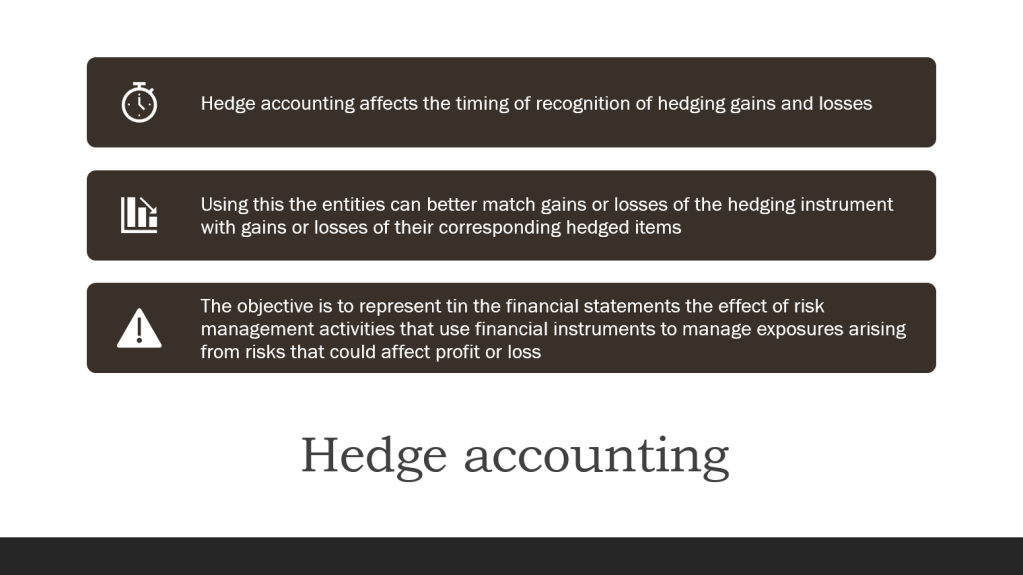

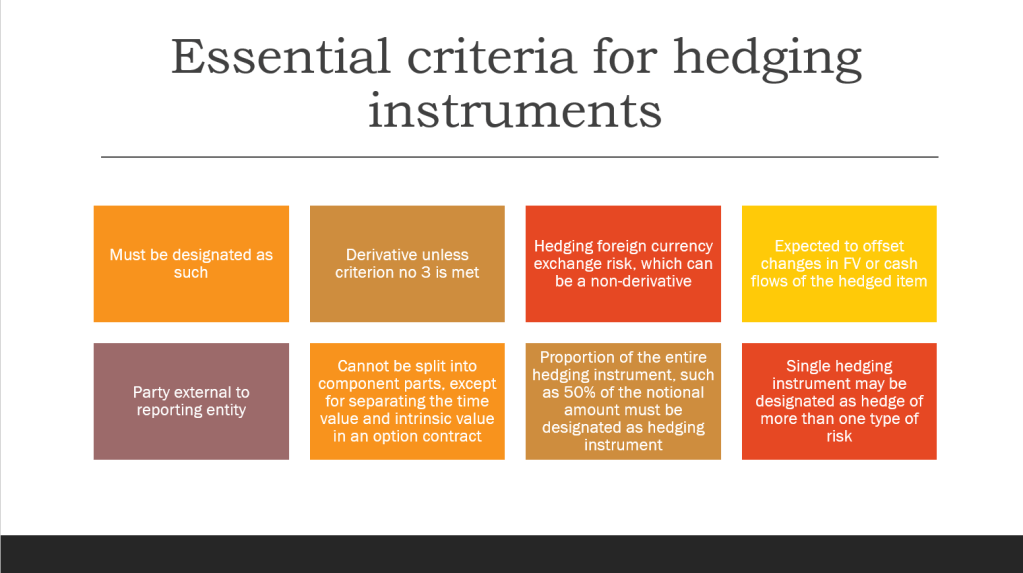

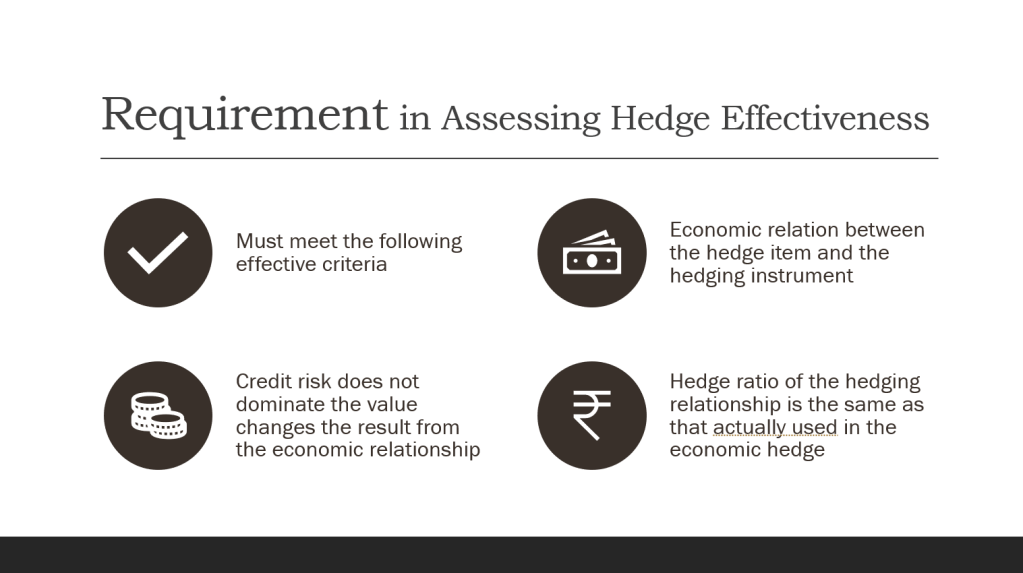
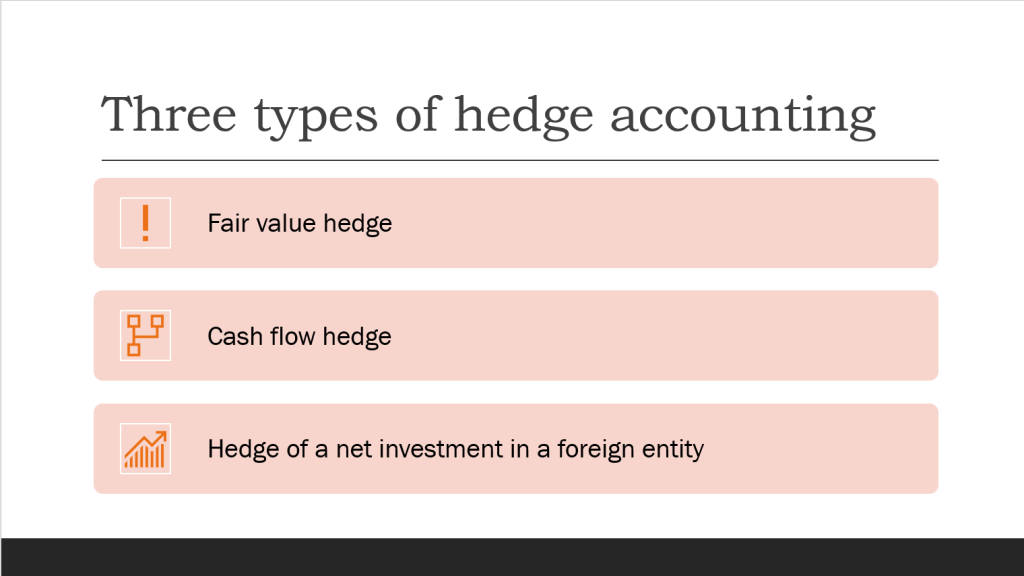

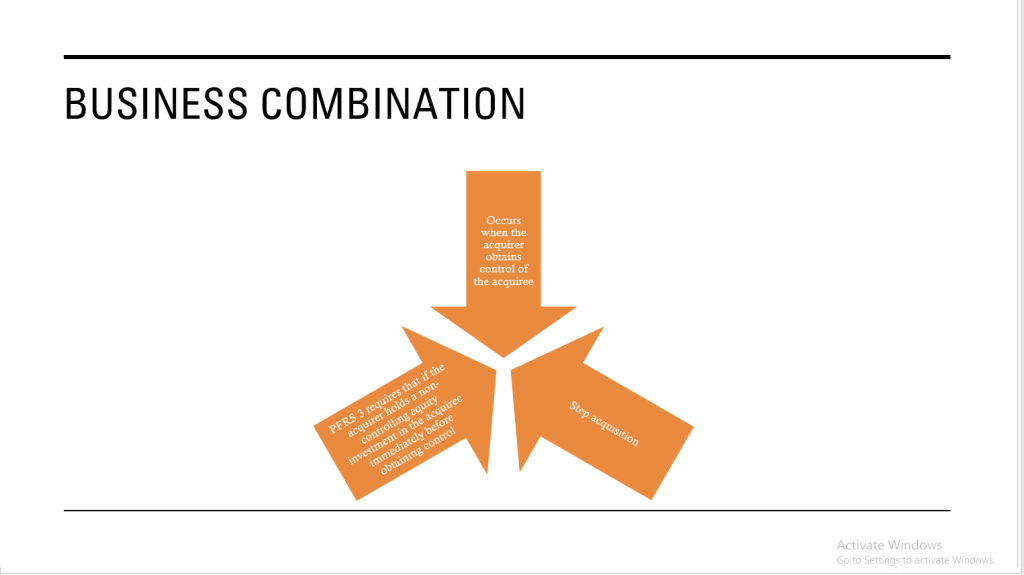

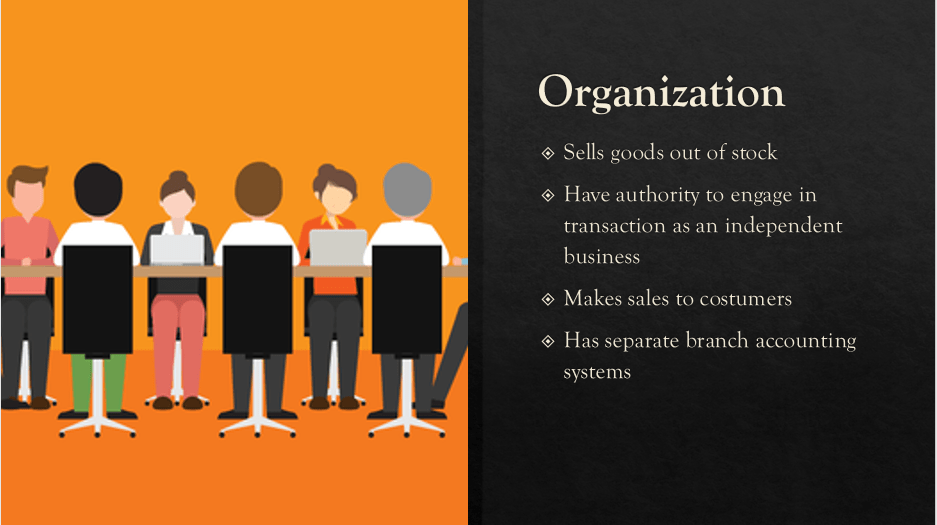
Business Combination as a transaction or other event in which an acquirer obtains control of one or more businesses. Transactions sometimes referred to as “true mergers” or “mergers of equals” are also business combinations
Structures of Business Combination
1.) Horizontal Integration – combination that involves companies with the same industry
2.) Vertical Integration – combination that involves companies that involves in the same industry but different levels
3.) Conglomerate Combination – involving companies in unrelated industries having little, if any, production or market similarities entering a new market
4.) Circular Combination – entails diversification

The Acquisition Method
Applied on the acquisition date which is the date the acquirer obtains control of the acquiree.
Statutory Merger
Acquiring company survives, whereas the acquired company ceases to exist
Example:
Business + Combination = Business Combination
Statutory Consolidation
It results when a new corporation is formed to acquire two or more corporations.
Example:
Business + Combination = AFAR
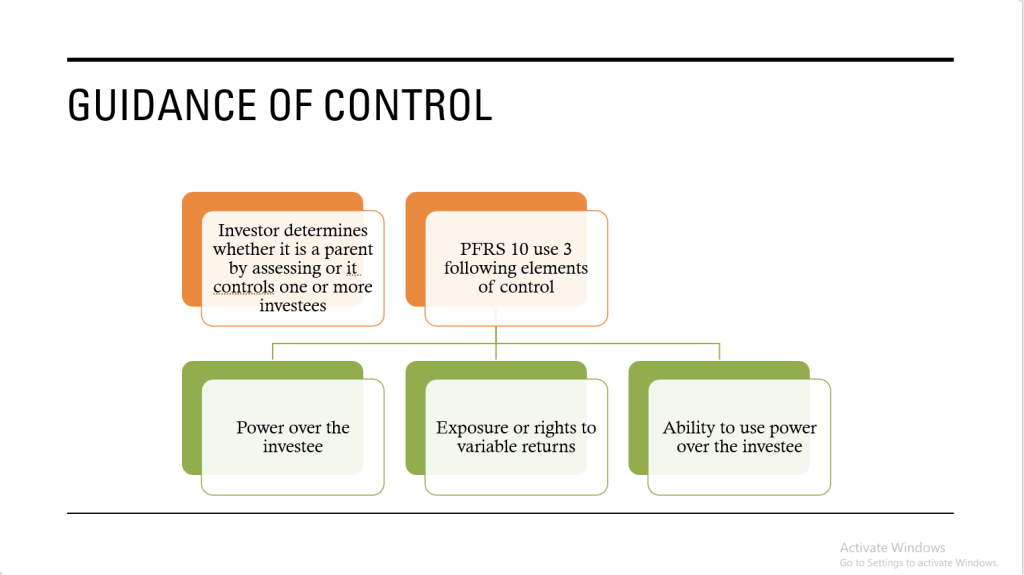
1.) Identify the acquirer
PFRS 3 paragraph 7 states that the acquirer is the entity that obtains control of the acquiree.


2.) Determine the acquisition date
PFRS 3 defines it as the date on which the acquirer obtains control of the acquiree
Dates that are important during the process of combination
-Date the contract is signed
-Date the consideration is paid
-Date nominated in the contract
-The date which assets acquired are delivered to the acquirer
-The date on which an offer becomes unconditional
3.) Calculating Fair Value of the Consideration Transferred
PFRS 3 paragrpah 7, the consideration transferred:
– measured at fair value at acquisition date
– calculated as the sum of the acquisition date fair value of
1.) the assets transferred by the acquirer
2.) the liabilities incurred by the acquirer to former owners of acquiree
3.) the equity interest issued by the acquirer
Consideration transfers
1.) Cash or other Monetary Assets
2.) Non-monetary Assets
3.) Equity Instruments
4.) Liabilities Undertaken
5.) Contingent Consideration
4.) Measurement Principle for Assets and Liabilities
– measured at fair value
Valuation Techniques
-Market approach
Uses prices and other relevant information generated by market transactions
-Income approach
Based on future economic benefit
-Cost approach
Reflects the amount that would be required currently to replace the service capacity of an asset
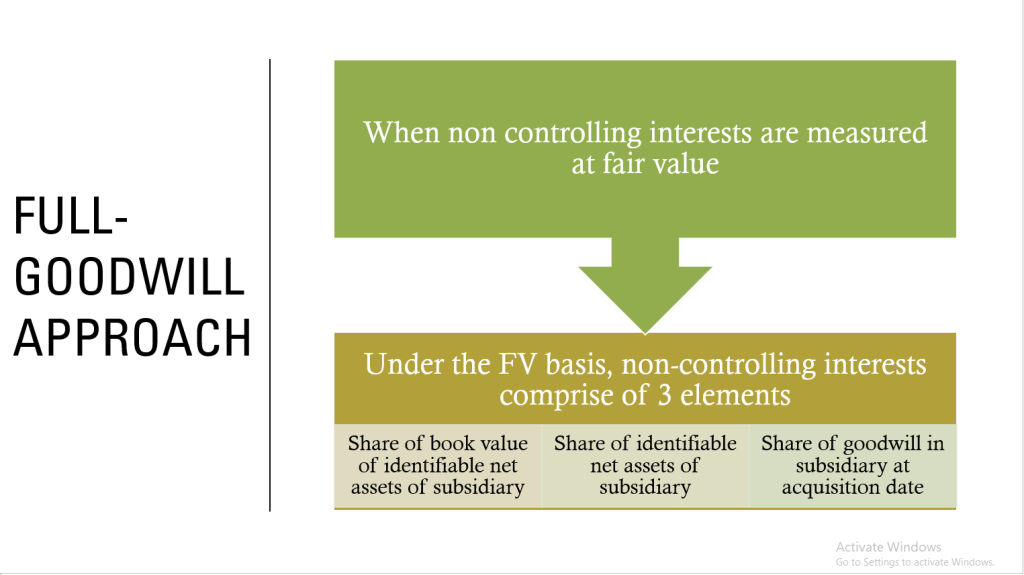
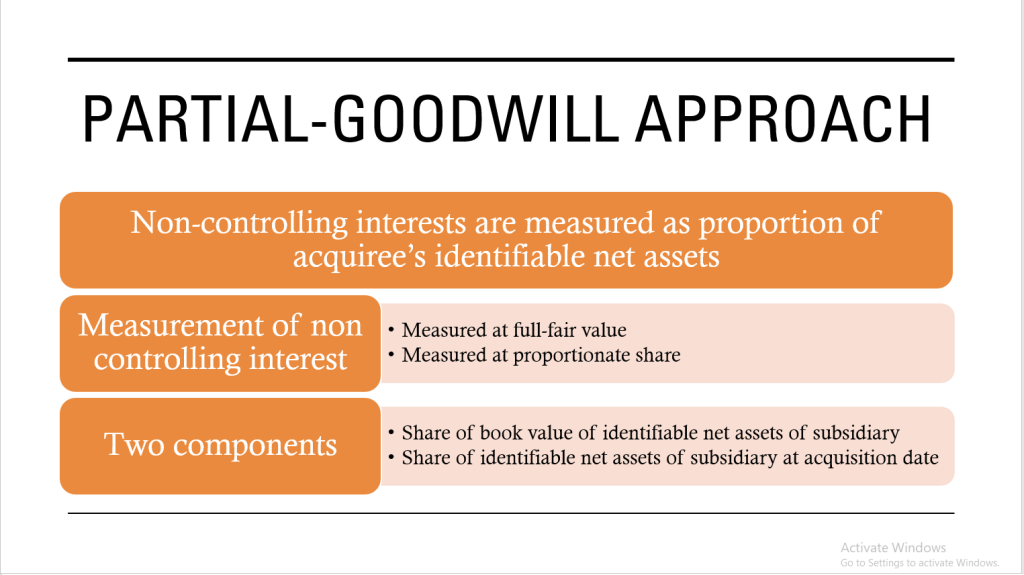
5.) Measure of goodwill
Goodwill
The acquirer shall recognize goodwill as of the acquition date, measured as the excess of (I) over (II) below:
I. The aggregate of
a.) The consideration transferred measured in accordance with this standard which requires acquisition date
b.) The amount of any non-controlling interest in the acquiree
c.) the acquisition date fair value
II. The net of the acquisition date amounts of the indentifiable assets acquire and the liabilites assumed measure in accordance with this standards
Items Included in Goodwill
1.) Assembled workforce of the acquiree
2.)Potential contractors
3.) Contingent Assets
4.) Future contracts renewal
Bargain purchase gain = Acquirer’s interest net fv of acquiree identifiable assets –
Consideration transferred





Every lesson takes time to master, so let’s go and study! #CPA
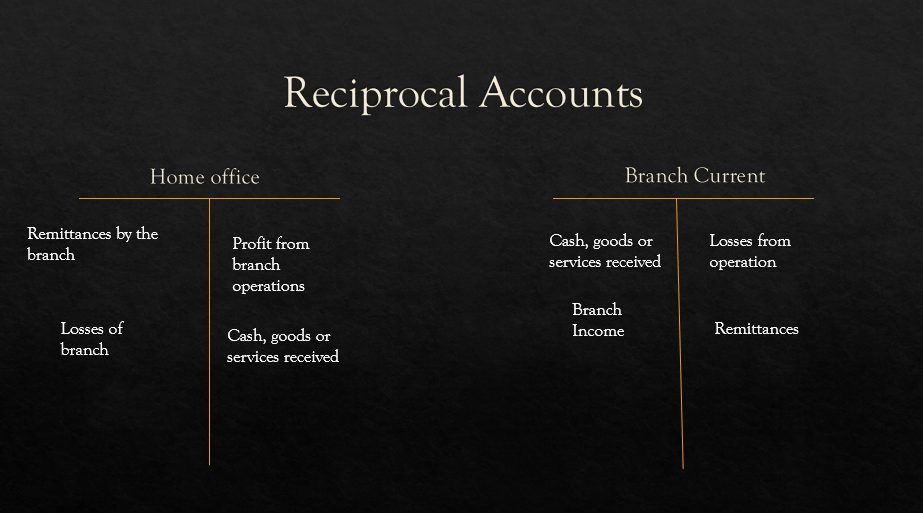
-Installment sales contract is a special type of credit arrangement which provides for a series of payments over a period of months or years
-Usually used by dealers in real estate, home appliances and cars
-The seller must wait for a considerable period of time to collect the full amount
Accounting Procedures
The gross profit from an installment sale is initially deferred and subsequently realized on a piecemeal basis.
Formula for installment payments are received
Realized gross profit = Collection on sale x Gross profit sale
Repossession
If a customer defaults on an installment contract and no further collections can be made the seller may repossess the property sold to satisfy the remaining indebtedness
The following procedures to record repossession may be used
1.) Record the repossessed merchandise in an appropriate inventory account in its fair value
2.) Cancel the uncollected installment receivable balance
3.) Write-off the balance of the deferred gross profit
4.) Recognize gain or loss

Trade-ins
They use trade-in as part of down payment.
General Rule
The actual value or the fair market value of asset received as a train should be used in valuing the said item
Different Conditions
1.) Trade in value is equal to actual value.
2.) Trade-in is greater than net realizable value.
The amount of the over allowance may be recorded either as charge to Over allowance on Trade-In account or Reduction from Installment Sales Account


Definition Treatment of a contract to last for a period of more than one year.
Recognizing the revenue based on PFRS 15
Types of construction contract
| Fixed priced contract | Cost-plus contact |
| A contract which the contractor agrees to a fixed price, subject to cost escalation clauses | A contract which the contractor is reimbursed for allowable or otherwise defined costs, plus a percentage of these costs or a fixed fee |

Percentage of completion / Overtime method
-Application of accrual assumption.
-Used when the outcome of the construction contract can be estimated reliably
-This approach avoids the mismatch between cost being recognized as they incurred
–Revenue is recognized when the contract is completed
Measuring earnings process
1.)Input Method
– Cost to Cost Method, the degree of completion is determined by comparing costs already incurred
Formula:

2.) Output Method
Measures are made in terms of results achieved

Point in time
-Used when the outcome cannot be reliably estimated
-Revenue is recognized when the performance obligation is satisfied.
Contract Revenue
Total amount of consideration receivable under the contract. It compromises of:
Variations – change in the scope of the work to be performed under the contract
Claims – amount that the contractor seeks to collect from the customer or another party as reimbursement for costs not included in the contract price

Definition
A contractual agreement with a franchisor to which the franchisor permits the franchisee to use the franchisor’s business name and/or trademark, manufacture or sell the franchisor’s products or services
Franchisor and franchisee are not partners, employer and employee, or principal and agent, but separate contracting parties
Four types of franchising agreement
Initial Franchise
The payment for establishing the relationship and providing services
Continuing Franchise
The payment received in return for the continuing rights such as management training, advertising and promotion, quality control, budgeting and others


Reasonably Assured, Not Reasonably Assured & Uncertain



It is the transfer of possession of merchandise without the transfer of title from the owner.
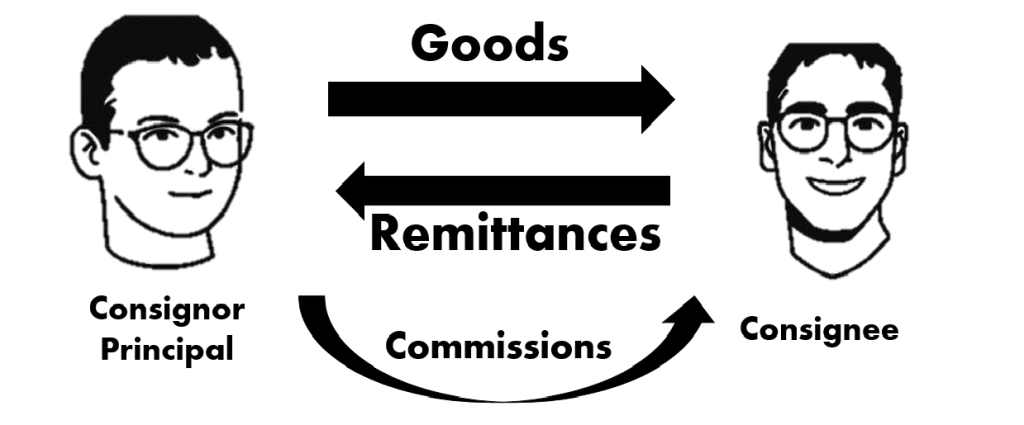

Now that we know the differences, let’s talk about the advantages of a consignment
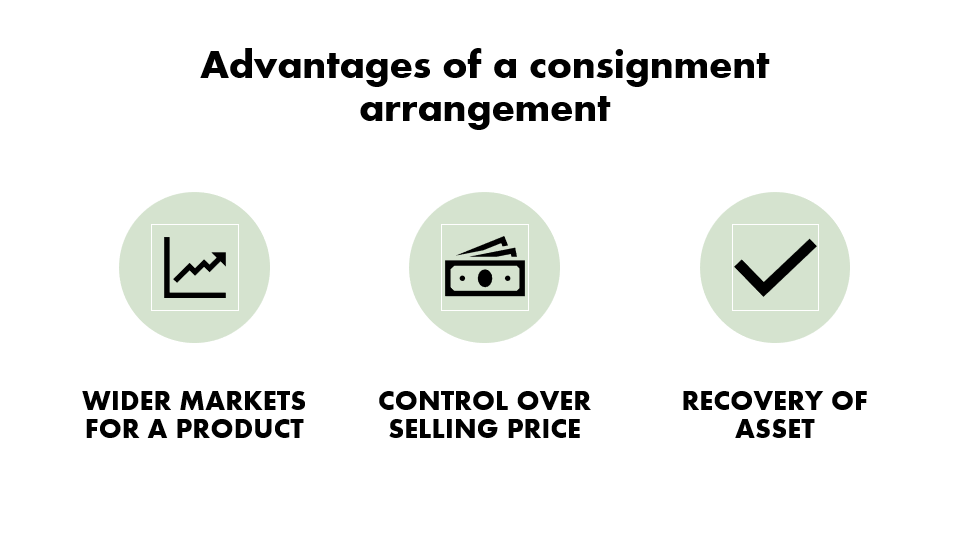

I think that consignment is quite easy to understand compared to other topics. Because we can easily connect to real life.
The new normal made me realize that it is very hard to be optimistic and motivated because of my energy comes my friends who really helps in both academic and life
“For the things we have to learn before we can do them, we learn by doing them.”


My learnings last meeting are as follows
1.) The difference between accounting income and taxable income
2.) Permanent differences does not give rise to deferred tax asset/ liability
3.)Recognition of tax asset / liability
4.) I realized that chapter 16 is about accounting for corporations that is why the rate is always 30%
5.) The difference between intraperiod and interperiod tax allocation
Something to share:
1.) I think that group quiz is more effective because it encourages students to ask questions
2.) I like how the class is being handled, we are learning a lot without so much pressure. Thank you ma’am!